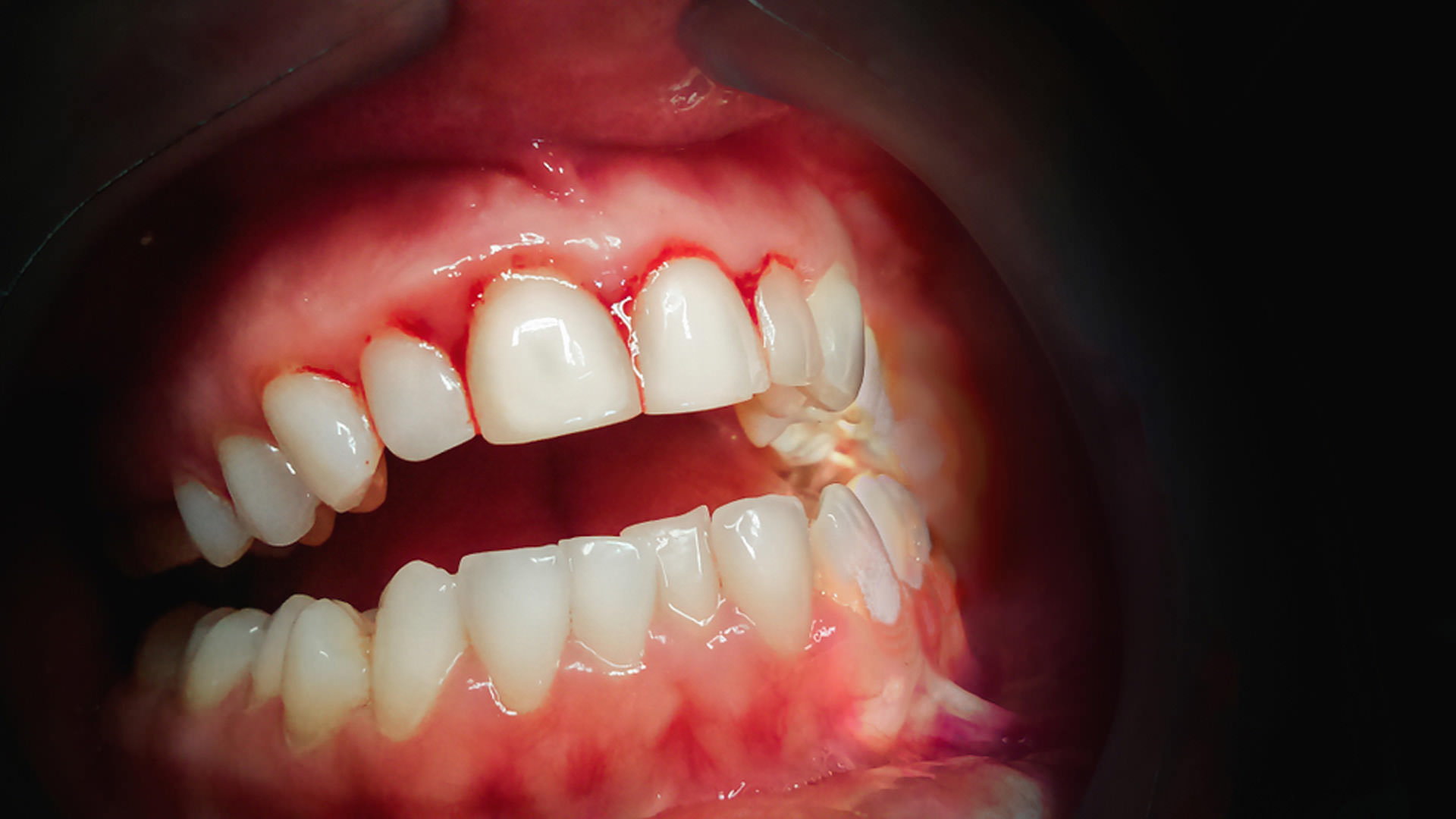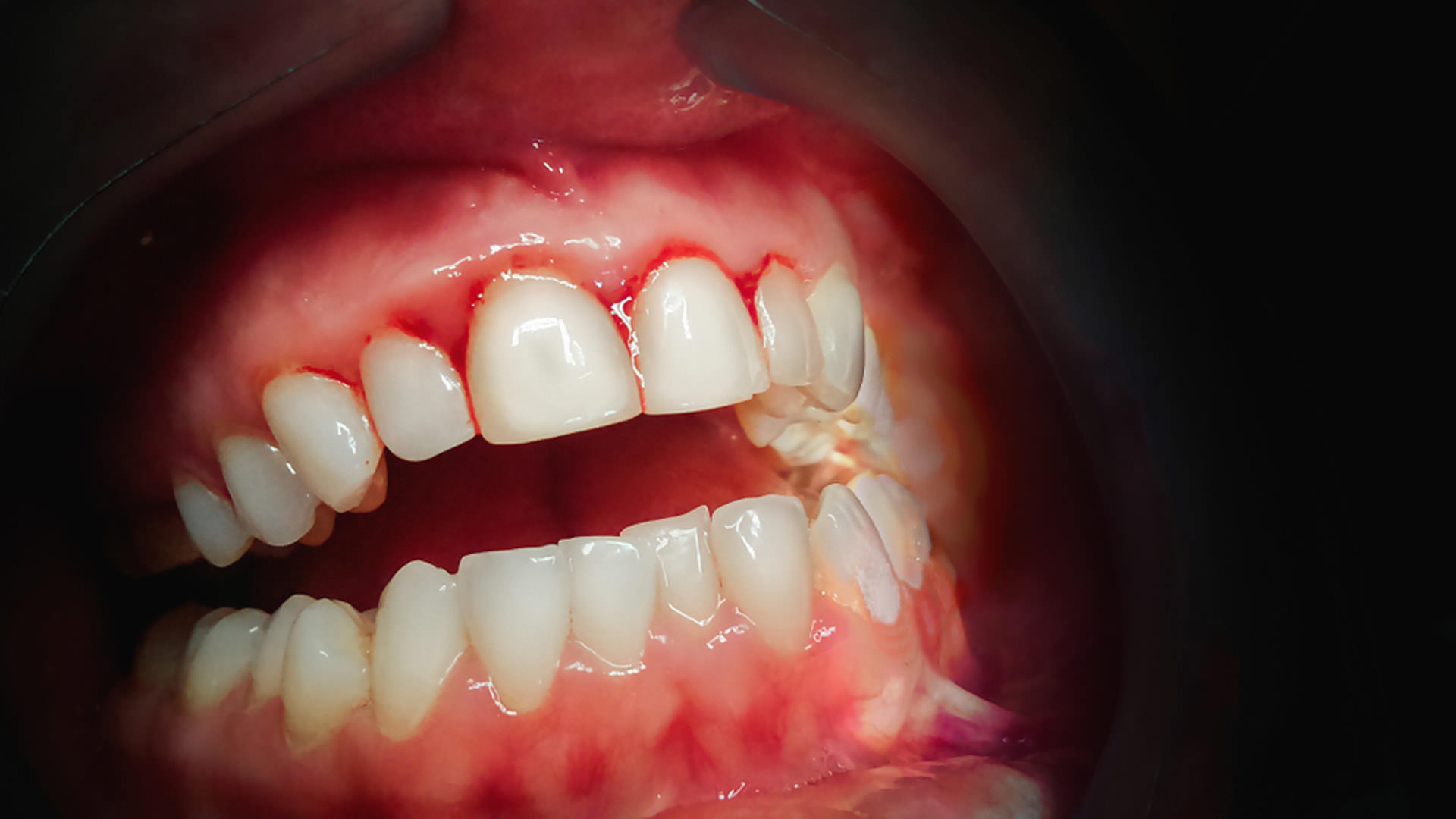
Paradontosis is a periodontal disease that arises as a result of a long-lasting inflammatory process caused by the presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the oral cavity. Bacteria accumulate in the interdental spaces and at the interface between the teeth and the soft tissue of the gums. The sediment created as a result of this process (so-called plaque) is transformed into tartar which causes irritation and painful swelling of the gums. Over time, the gums shrink to expose the dental necks, which become very sensitive to temperature changes and to sweet and sour foods (extremely painful condition). If the process is not identified and stopped in time, the teeth lose their proper attachment in the jaw and they just start to fall out.
Symptoms of periodontosis:
• red, swollen and oversensitive gums,
• bleeding from the gums,
• loose teeth,
• bad breath,
• unpleasant taste in the mouth,
Important – periodontitis may occur without obvious symptoms.
Why it is important to follow the periodontal treatment?
Untreated periodontal disease has a tendency to deepen. The gaps between gums and teeth (so-called periodontal pockets) can be infected at the later stages of the disease. Over time, the teeth get loose and they need to be extracted.
Causes of periodontitis
The main cause of the gum disease is the reaction of gums to the bacterial plaque, which is constantly formed on teeth. Plaque can be removed from the tooth surface using a brush and dental floss. If the plaque is not removed in time, it gets transformed into a hard substance called tartar. At this stage dentist or dental hygienist must intervene to remove tartar with specialized dental tools.
Factors conducive to gum disease:
• smoking tobacco
• diabetes
• stress
Some people are more susceptible to periodontal disease than others. The patient may not notice any worrying symptoms, however, regular visits to the dentist allow early detection of a possible threat.
Treatment of periodontitis
The treatment of periodontitis differs depending on the current stage of the disease. The basic treatment, so-called scaling of teeth, is consisting of accurate removal of dental plaque and tartar from above and below the gum. Antibacterial treatment or even gum surgery may also be involved. Your dentist will diagnose the stage of the disease and discuss the details of treatment with you.
How to prevent the gum disease
The basic preventive action is regular removal of the dental plaque from teeth and gums using a toothbrush and dental floss. Your dentist or hygienist (therapist) will advise you on the most appropriate methods.